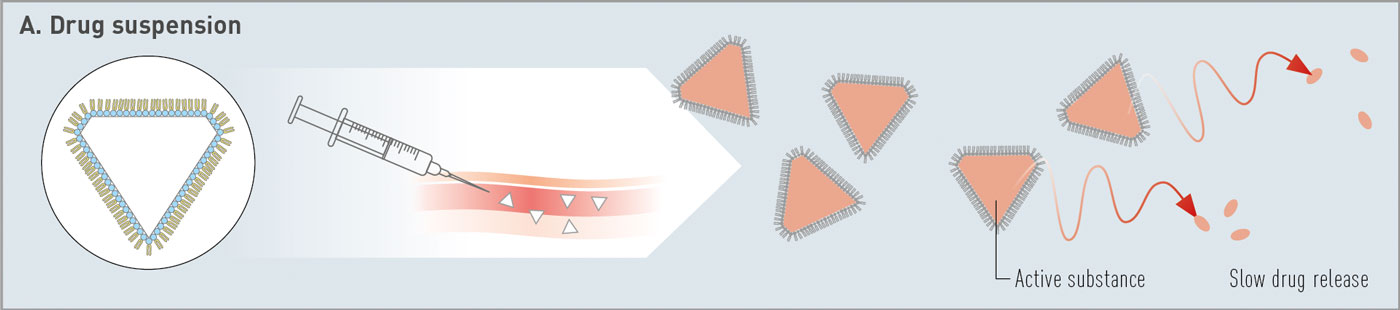
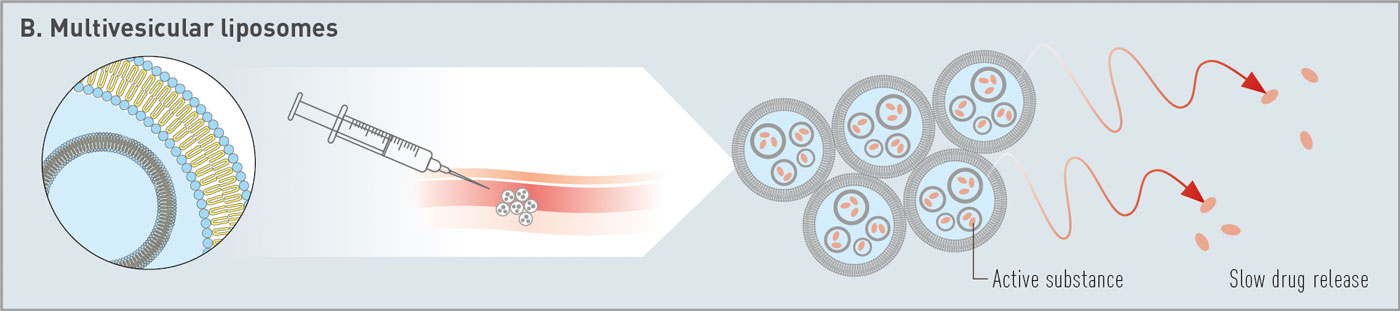
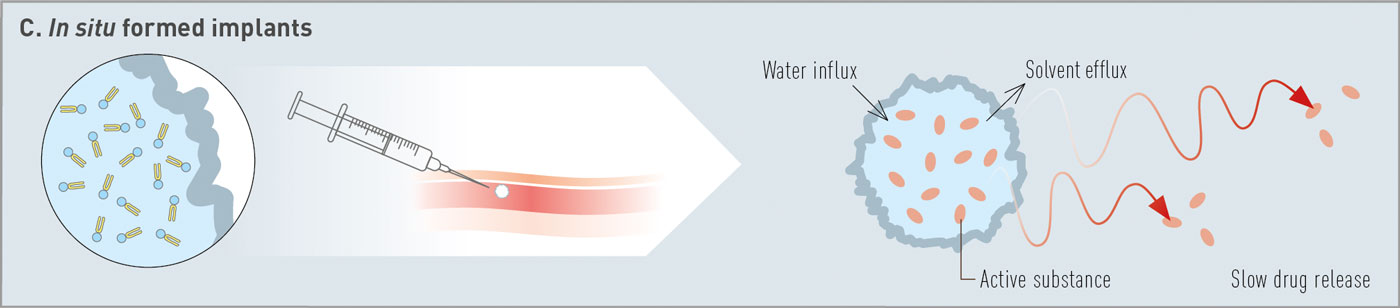
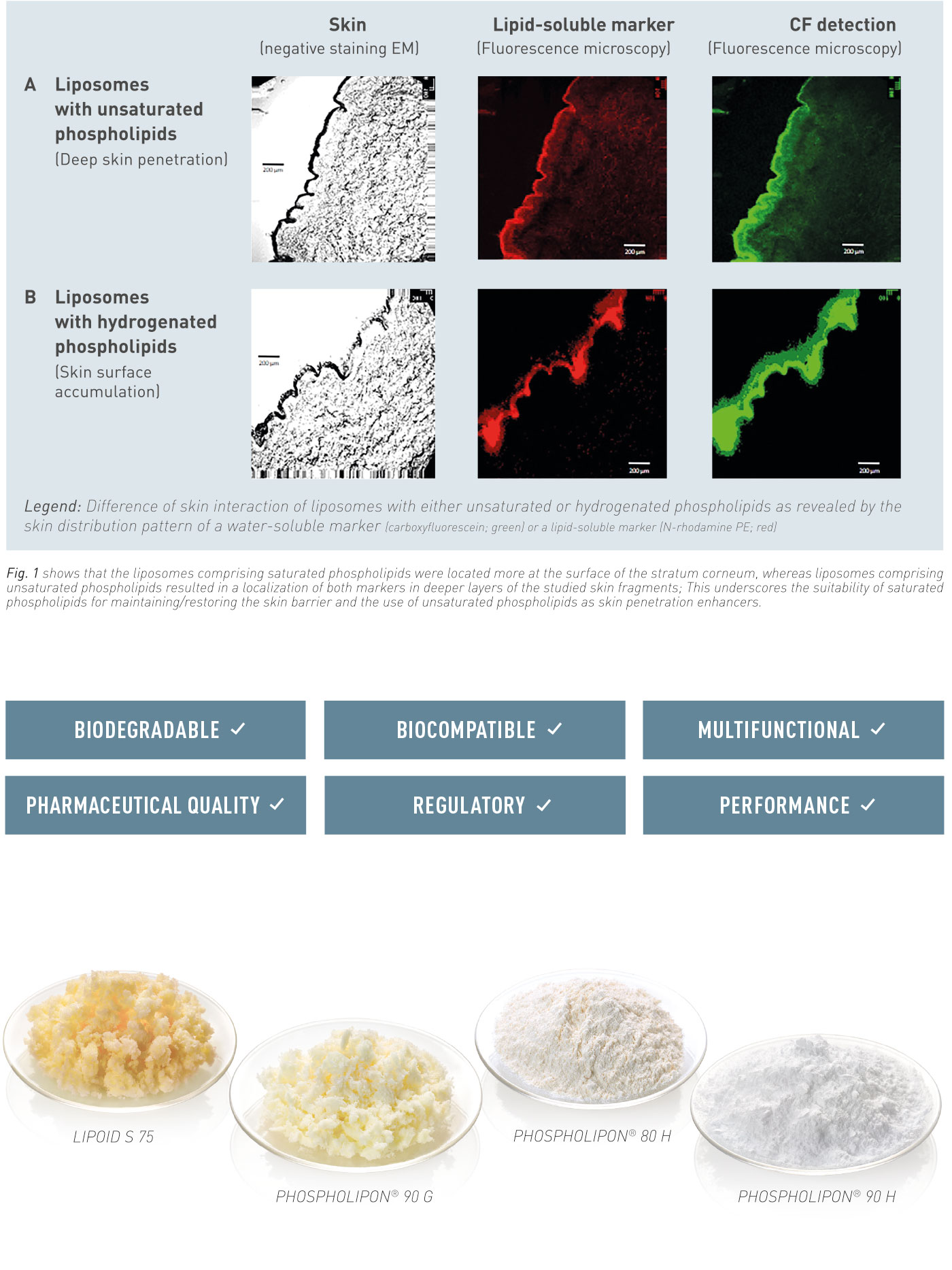
Lipoid präsentierte natürliche und synthetische Phospholipide für innovative Arzneimittelverabreichungssysteme, die Impfstoffe, pulmonale Anwendungen und Depotformulierungen umfassen. Vielen Dank an alle Teilnehmer, das außergewöhnliche Interesse an unseren Materialien – cGMP-Phospholipide für Ihre Produkte von der Forschung bis zur Vermarktung – und die ergiebigen Diskussionen.
Das „Annual Skin Forum 2022“ bringt international anerkannte Experten aus der ganzen Welt zusammen, um die Hautforschung durch Wissens- und Informationsaustausch voranzubringen.
Jedes Jahr organisiert das Hautforum ein Treffen mit angesehenen Hauptrednern sowie Studenten, Klinikern, Wissenschaftlern und Interessenvertretern aus der Industrie, um die neuesten Forschungsergebnisse und regulatorischen Entwicklungen zu diskutieren.
Beim „13. Drug Delivery and Formulation Summit“ werden die aufregendsten und innovativsten Entwicklungen in der pharmazeutischen Technologie präsentiert. Themen des diesjährigen Treffens sind die neuesten Trends, Konzepte und Innovationen der pharmazeutischen Industrie, wie:
• Formulierungsdesign für schwer lösliche Wirkstoffe
• Potenzial der Nanotechnologie für bessere Dareichungsformen
• Die neuesten Technologien zur kontrollierten Freisetzung
• u. v. m.
Als einer von über 1.200 Ausstellern präsentierte sich Lipoid auf der weltweit führenden Veranstaltung für Lebensmittelzutaten, Wirkstoffe und Rohstoffe, Nahrungsergänzungsmittel und Dienstleistungen, an der rund 25 000 Fachleute aus der Ernährungsbranche teilnahmen.
Die diesjährige Messe, die alle Akteure einer sich ständig wandelnden Nahrungsergänzungsmittelbranche zusammenbringt, hat vom 10. bis 12. Mai 2022 in den Hallen 2, 4, 5 und 6 des Palexpo Messe- und Kongresszentrums stattgefunden und war ein voller Erfolg.
Langjährig bestehende Kontakte konnten vertieft und viele neue geknüpft werden. Dabei hat sich gezeigt, dass das Konzept, neben den natürlichen Rohstoffen auch fertige Systeme anzubieten, voll aufgegangen ist.
Insbesondere unsere Trägersysteme waren von großem Interesse, da sie den Kunden eine schnelle und einfache Produktentwicklung ermöglichen. Flüssige Formulierungen mit fettlöslichen Aktivstoffen wie z.B. Coenzym Q10, Curcumin oder Omega-3-Fettsäuren sowie liposomales Vitamin C sind ohne zusätzliche Herstellschritte zur direkten Abfüllung verfügbar.
Für individuelle Lösungen erfreuen sich unsere vorformulierten Liposomen oder Phospholipid-Pflanzenöl-Mischungen großer Beliebtheit. Diese Trägersysteme lassen sich einfach in Formulierungen einarbeiten oder sind direkt zur Abfüllung geeignet.
Egal ob fertig beladen oder als Eigenentwicklung – unsere Phospholipide überzeugen durch Ihre Natürlichkeit und ermöglichen eine erhöhte orale Bioverfügbarkeit von Wirkstoffen ohne Einsatz chemisch hergestellter Zusatzstoffe.
Vom 28. bis 31. März begrüßte Lipoid seine Kunden und Freunde an seinem Stand auf dem 13. PBP World Meeting in Rotterdam. Diese Konferenzreihe gewinnt unter den pharmazeutischen Wissenschaftlern immer mehr an Bedeutung: Mit fast 1000 eingereichten Abstracts und mehr als 1300 Teilnehmern hat sie sich zu einer etablierten Großveranstaltung entwickelt, die Wissenschaftler aus der ganzen Welt anzieht.
Wichtig ist, dass das gesamte Themenspektrum in den Bereichen Pharmazie, Biopharmazie und pharmazeutische Technologie abgedeckt wird. Dazu gehören beispielsweise technische Aspekte der Herstellungsverfahren, die Palette der kommerziell erhältlichen Hilfsstoffe, die die Formulierung einer Vielzahl von Arzneimitteln und Medizinprodukten ermöglichen, die zugrunde liegenden Grundlagenwissenschaften (z. B. physikalisch-chemische Prinzipien), modernste Techniken zur Charakterisierung von Darreichungsformen in vitro und in vivo sowie potenzielle Fallstricke und Hürden, die bei der Produktentwicklung, Herstellung und Qualitätskontrolle zu überwinden sind.
Spatenstich in Köln am 19. Januar 2022
Der Ludwigshafener Konzern Lipoid, der weltweit die Pharmaindustrie mit Hilfsstoffen beliefert und vier unabhängige Produktionsanlagen in Deutschland betreibt, setzt kontinuierlich auf Wachstum.
An seinem Kölner Standort, der PHOSPHOLIPID GmbH, wird mittelfristig ein dreistelliger Millionenbetrag zur Errichtung eines modernen Produktions- und Laborkomplexes, eines pharmazeutischen Lagers, sowie einer neuen Dampf- und Kühlwassererzeugung auf insgesamt über 15.000 m2 Grundfläche investiert.
An der Realisierung dieses Projekts arbeitet ein interdisziplinäres Team von über 20 Mitarbeitern aus den Bereichen Technik, Qualitätssicherung, Qualitätskontrolle, Produktion und Einkauf zusammen mit lokalen Architekten, Fachplanern und Experten.
Trotz des Einflusses der COVID-Pandemie und der damit verbundenen veränderten Rahmenbedingungen während den laufenden Planungsphasen, die z. B. zeitweise zu einem Verzicht auf persönliche Besprechungen geführt haben, konnten die vorbereitenden Maßnahmen, nach Genehmigung des vorzeitigen Baubeginns im März 2021, in weniger als 12 Monaten abgeschlossen werden. Das ermöglichte die planmäßige Durchführung des symbolischen Spatenstichs bereits im Januar 2022 – zusammen mit Vertretern aus der lokalen Politik, der unmittelbaren Nachbarschaft, sowie dem Projektteam.
Die Inbetriebnahme der Dampf- und Kühlwassererzeugung wird noch in diesem Jahr erfolgen. Die Fertigstellung des Logistikgebäudes ist bereits für das erste Quartal 2024 vorgesehen. Die Bereiche für die Qualitätskontrolle, Qualitätssicherung sowie Verwaltung sollen bis spätestens Ende 2024 bezugs-fertig sein. Die Inbetriebnahme des Produktionsgebäudes erfolgt ebenfalls im vierten Quartal 2024. Mit der geplanten Prozess- und Anlagentechnik möchte die Unternehmensgruppe die Kapazitäten dieses Standortes erheblich erhöhen und gleichzeitig die Einhaltung der selbst gesteckten Nachhaltigkeitsziele sicherstellen.
Nach Aussage des Gesamtprojektleiters Dr. Lorenz Gabel basieren diese Investitionsvorhaben auf einer klaren Entscheidung der Lipoid-Gruppe, den bestehenden Standort langfristig zu entwickeln.
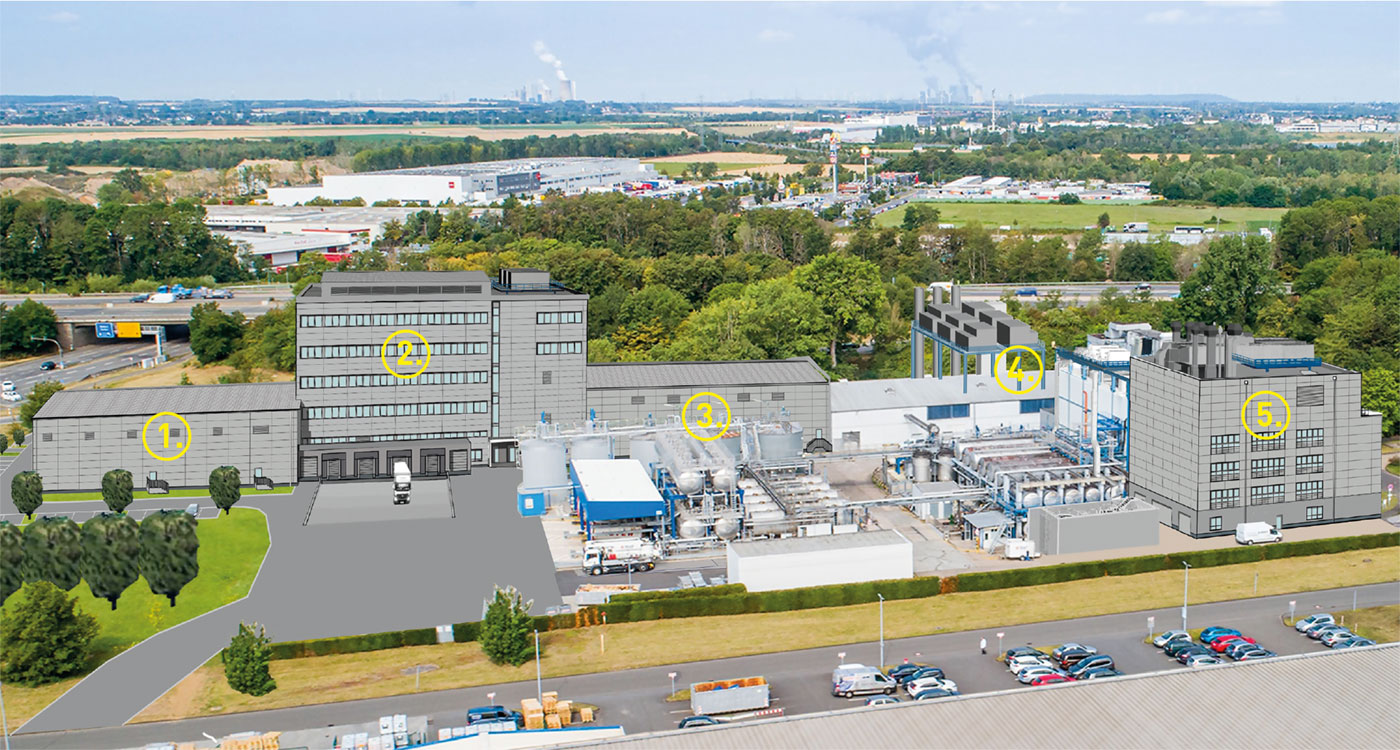
Abbildung 1: 1. bis 3. Pharmazeutischer Lager- und Laborkomplex, 4. Dampf- und Kühlwassererzeugung, 5. Produktionsgebäude