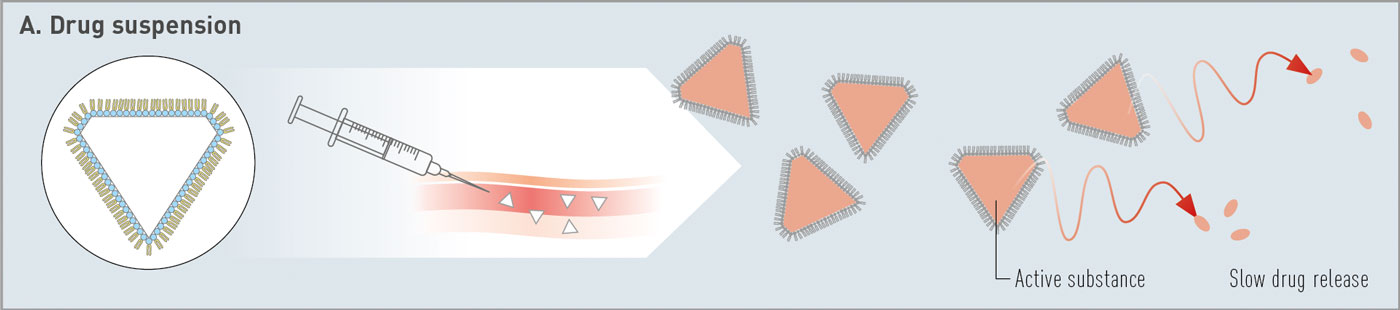
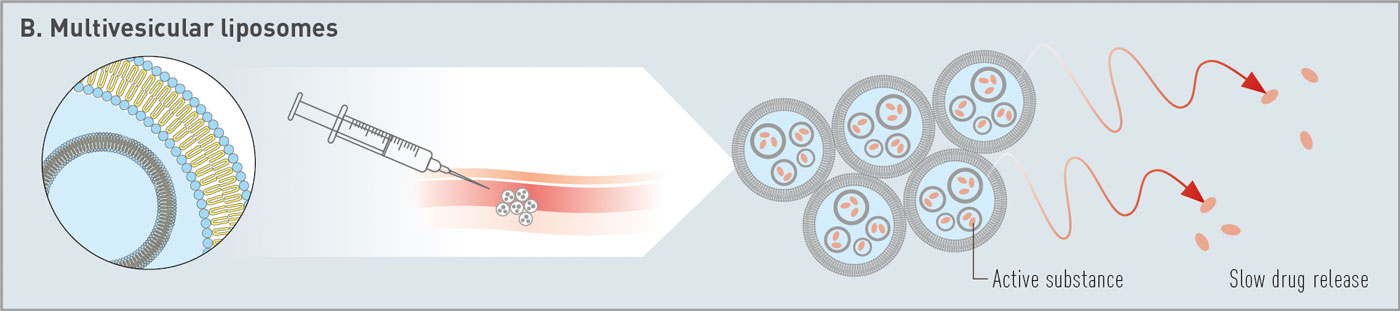
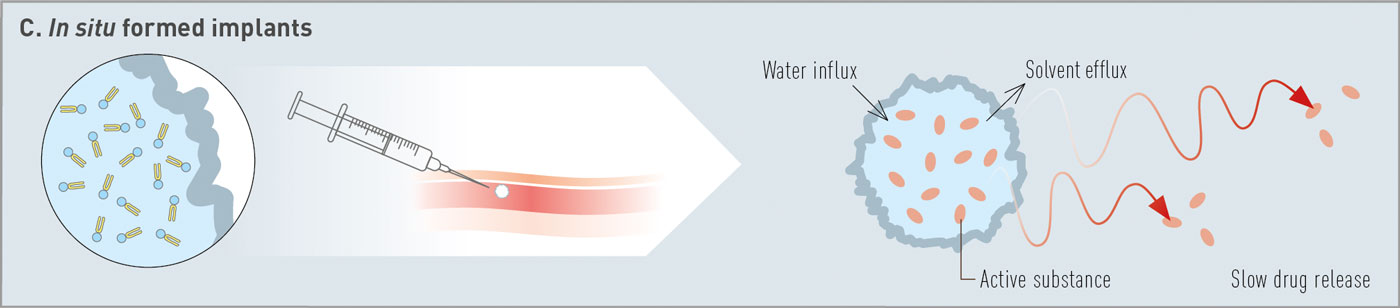
At the „Good Morning Meeting“ in Copenhagen
Lipoid presented on natural and synthetic phospholipids for innovative drug delivery systems, covering vaccines, pulmonary applications and depot formulations. Thanks a lot to all attendees, the exceptional interest in our materials – cGMP phospholipids for your products from R&D to commercialization – and the fruitful discussions.
The Skin Forum brings together internationally recognised experts from all over the world to advance skin research through knowledge and information exchange.
Each year, the Skin Forum organises an annual meeting with distinguished keynote speakers as well as students, clinicians, scientists and industrial stakeholders to present and discuss the latest research outcomes and regulatory developments.
The „13th Drug Delivery and Formulation Summit“ is all about showcasing the most exciting and innovative developments in pharmaceutical technology.
The 2022 Summit covers small molecules and biologics, new technologies, concepts and case studies in areas such as:
• Formulation design for poorly soluble compounds
• The potential of nanotechnology for better deliverability
• The latest controlled released technologies
• and many more
Lipoid was one of more than 1,200 exhibitors participating in this world-leading event for food ingredients, actives and raw materials, dietary supplements and services, which was attended by around 25,000 nutrition industry experts.
Bringing together all stakeholders in a constantly evolving dietary-supplement sector, this year’s show took place in Halls 2, 4, 5, and 6 of Geneva’s Palexpo Exhibition and Congress Center on May 10 to 12, 2022, and was a resounding success.
Longstanding contacts could be revived and intensified and many new contacts forged. Moreover, the concept of offering not only natural raw materials but also ready-to-use systems was seen to be fully justified.
In particular, our carrier systems attracted considerable interest because they facilitate fast and straightforward product development. Liquid formulations containing fat-soluble active ingredients such as coenzyme Q10, curcumin, or omega-3 fatty acids, as well as liposomal vitamin C, are available for direct bottling, obviating any need for additional manufacturing steps.
Our preformulated liposomes or phospholipid-vegetable oil mixtures have proved to be extremely popular for developing individual solutions. They constitute versatile carriers for a wide range of active ingredients introduced into formulations simply by stirring.
Whether preloaded systems or products of in-house development – our phospholipids excel by virtue of their natural characteristics and provide enhanced oral bioavailability without any need for synthetically produced additives.
Between March 28th and 31st Lipoid welcomed its customers and friends at their booth on the 13th PBP World Meeting in Rotterdam. This conference series is continuously gaining in impact among the pharmaceutical scientists: With close to 1000 submitted abstracts and more than 1300 participants it has become a well-established major meeting, attracting scientists from all over the world.
Importantly, the entire spectrum of topics in the fields of Pharmaceutics, Biopharmaceutics and Pharmaceutical Technology will be covered. This includes for example engineering aspects of manufacturing processes, the portfolio of commercially available excipients enabling formulation of a large variety of drug products and medical devices, the underlying basic sciences (e.g., physico-chemical principles), cutting-edge characterization techniques of dosage forms in vitro and in vivo, as well as potential pitfalls and hurdles to be overcome during product development, manufacturing and quality control.
Groundbreaking Ceremony at Cologne on January 19, 2022
The Ludwigshafen-based Lipoid enterprise, which supplies excipients to the global pharmaceutical industry and operates four independent production facilities in Germany, remains on a continuous growth track. A medium-term investment in the triple-digit million-Euro range is currently underway at the company’s Cologne site, PHOSPHOLIPID GmbH, to construct a modern production and laboratory complex, a pharmaceutical warehouse, and a new steam generation and cooling water unit, all on a total area in excess of 15,000 m2.
Implementation of this project is in the hands of a 20-person interdisciplinary team covering the areas of engineering, quality assurance, quality control, production, and procurement, which is working together with local architects, specialist planners, and other experts.
The impact of the COVID pandemic and resulting changes in working conditions during the planning phases led to cancellation of face-to-face meetings. However, preparatory measures could be completed in less than 12 months following approval of the early start of construction in March 2021. This allowed the symbolic groundbreaking ceremony to take place as early as January 2022 – with participation of local politicians, representatives from the immediate neighborhood, as well as the project team.
Commissioning of the plants for steam and cooling water generation will follow in the course of this year. Completion of the warehouse building is already planned for the first quarter of 2024. The areas for quality control, quality assurance, as well as administration should be ready to move in by the end of 2024 at the latest. Commissioning of the production building is likewise scheduled for the fourth quarter of 2024.
Through implementation of the planned process and plant engineering, the corporate group intends to substantially enhance the capacity of this site while simultaneously complying with its self-imposed sustainability goals.
According to the overall project manager Dr. Lorenz Gabel, these investment projects are based on a clear decision of the Lipoid Group to pursue long-term development of the existing site.
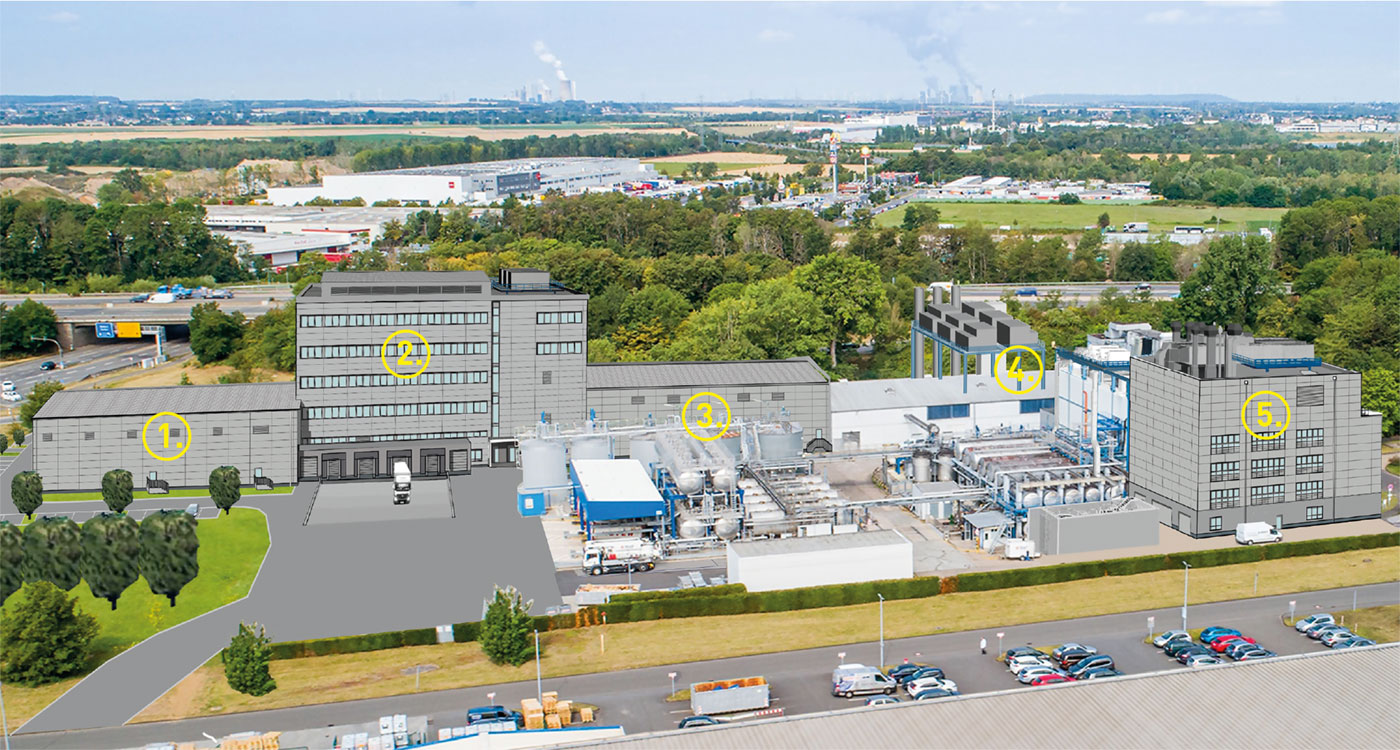 Fig. 1: 1. to 3. Pharmaceutical warehouse and laboratory complex, 4. Steam generation and cooling water plant, 5. Production building
Fig. 1: 1. to 3. Pharmaceutical warehouse and laboratory complex, 4. Steam generation and cooling water plant, 5. Production building