Poor solubility, slow dissolution rate, gastrointestinal degradation, and low permeability are typical factors that limit oral bioavailability of drugs. In order to overcome these limitations advanced formulations with phospholipids can be used. Phospholipids are diversely used as excipients in such formulations as dispersing agents, emulsifiers, or as additional or sole matrix components for solid dispersions (Fig. 1). Liposomes dissociate in the gastrointestinal tract and release phospholipids, which provide solubilising effects.
Moreover, phospholipids are applied as technical excipients in tablet coatings or as processing aids to produce soft gel capsules.
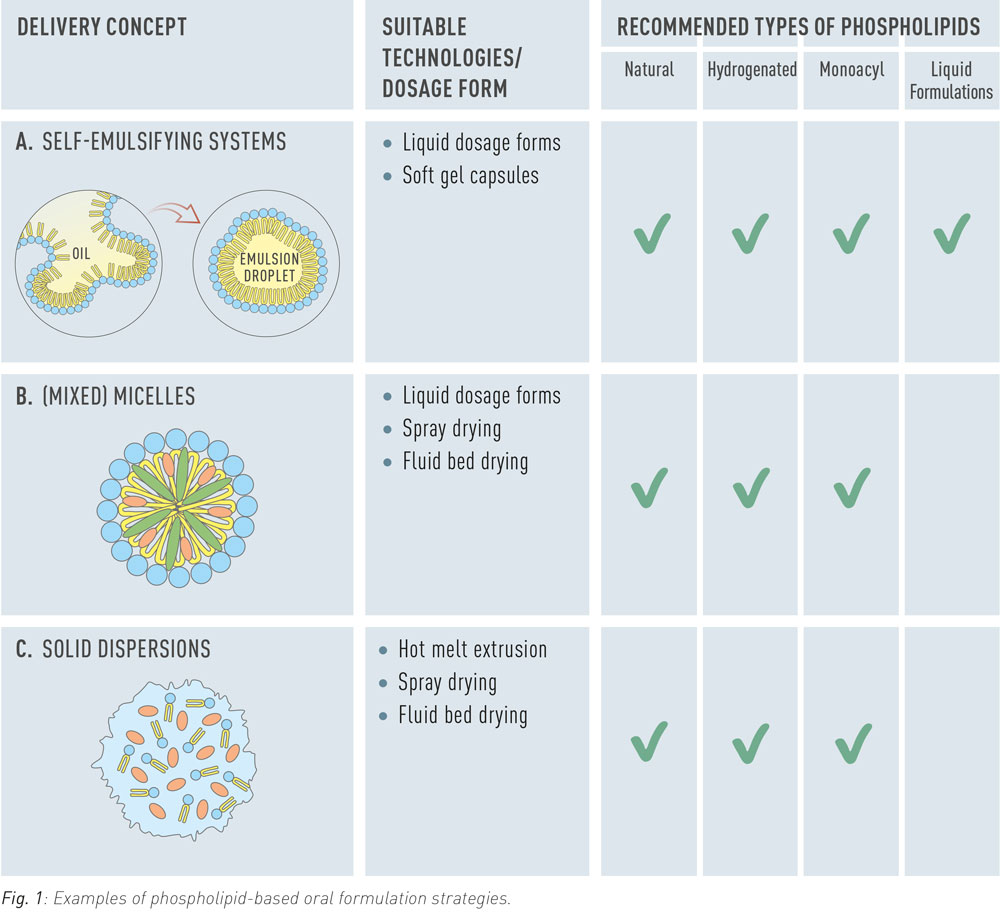
Self-Emulsifying Systems
Self-emulsifying systems (often referred to as SEDDS) are water-free formulations that spontaneously form emulsions in aqueous media, including gastrointestinal fluids. They are used predominantly for solubilization of lipophilic drugs to increase their bioavailability. In formulations for oral ingestion, self-emulsifying systems are typically applied as oily liquid or in form of a soft gel capsule. The preconcentrate can be administered in its water-free form but may also be diluted in an appropriate beverage before administration.
Mixed Micelles
In the gastrointestinal tract, mixed micelles composed of endogenous phospholipids and bile salts solubilize lipophilic nutrients to make them available for absorption. Pharmaceutically applied mixed micellar formulations consist of soybean phosphatidylcholine and therefore offer a natural vehicle for lipophilic drugs such as Vitamin K.
Solid Dispersions
Solid dispersions are widely employed to enhance the dissolution of poorly soluble crystalline drugs by amorphization of the drug substance. Phospholipids are investigated as complementary or sole matrix material for this purpose. In addition to amorphization, phospholipids contribute to drug solubilization by enhancing wettability, forming colloidal structures upon hydration and stimulating the secretion of bile.
Concluding Remarks
Phospholipids are multifunctional excipients with versatile applications in oral formulations. Their physiological role in digestion and absorption processes underscores their biocompatibility, functionality, and safety.