COMMITMENT TO INNOVATIONS
Phospholipids as physiological components
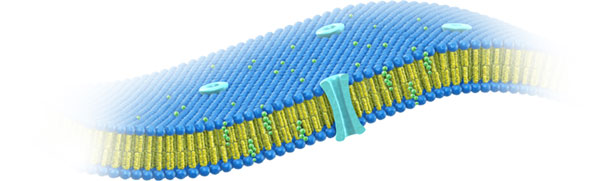
Phospholipids are essential components of the cell membrane, contributing to the function of every living cell. They are main components of lipoprotein particles, play an important role in the endogenous transport of lipids, contribute to blood coagulation and bone formation and many more physiological functions. Furthermore, phospholipids can be found in bile in the gastrointestinal tract and are therefore crucial for the digestion and absorption of lipophilic compounds. Nonetheless, they are a source of essential nutrients such as choline and essential polyunsaturated fatty acids.
Based on their unique physicochemical properties, phospholipids are multi-purpose excipients for a wide range of pharmaceutical applications. Related to their physiological function, they are biocompatible, biodegradable, and safe for any administration route. Phospholipids have a long history of use as essential excipients in many worldwide marketed drugs products.
Therefore, based on these unique characteristics, phospholipids are ideal excipients for state-of-the-art pharmaceutical dosage forms and innovative drug delivery systems.
Schematic depiction of phospholipids
What are phospholipids?
The molecular structure of phospholipids comprises a glycerol backbone esterified with fatty acids and phosphate. The systematic designation of, e.g., phosphatidic acid (PA) is 1,2-diacyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphate. The phosphate group of PA can be further esterified, for instance in phosphatidylcholine (PC) with choline, in phosphatidyl-ethanolamine (PE) with ethanolamine, in phosphatidylglycerol (PG) with glycerol, and in phosphatidylserine (PS) with serine.
Depending on the structure of the polar region and the pH of the medium, phospholipids can be zwitterionic (neutral) or anionic. PC and PE are zwitterionic and have a neutral charge at pH 7. PA, PG, and PS are examples of anionic phospholipids. Natural cationic phospholipids do not exist, but synthetic lipids fill this gap and have a positive net charge.
Moreover, phospholipids show a high diversity of fatty acids attached to the glycerol backbone. The phospholipids may contain one or two fatty acids, which are saturated, mono-unsaturated, or polyunsaturated. The fatty acid chain length, their degree of unsaturation, and the various possible head groups affect the physicochemical properties of the phospholipids such as phase transition temperatures, formation of mesophases (e.g. micelles, inverted micelles, liposomes), appearance, solubility, and miscibility.
Combining the many different head groups and fatty acid tails, an almost unlimited number of possible phospholipids exists.
Molecular structure of phosphatidylcholine, a typical phospholipid.
Schematic illustration of the most common phospholipids found in natural sources.
Our modern life-science industry and other key industries rely on innovative and state-of-the-art materials.
With the continuous development of new products and formulations, we pave the way to a sustainable future – not only for the pharmaceutical, but also for the health, nutrition, and cosmetics industries.
As one of the major players in the fascinating world of phospholipids, we at Lipoid are constantly pushing the boundaries in the development and production of (phospho)lipids towards greater innovation, efficiency, and sustainability. A steadily growing portfolio and a broad and powerful network between our R&D department, researchers, and universities around the world constitute the backbone of our innovative strength. Innovation, however, means more to us than the simple development of novel materials or products. We are also setting standards in terms of customer-oriented services, new business models, and process efficiency. We endorse and support all kinds of innovation if they will create new values – whether in terms of growth, social and environmental benefits, or ideally a combination of all these. Our concept of open innovation has the potential to significantly enrich traditional processes by integrating knowledge from external sources: new perspectives and the early inclusion of customer needs can reduce the innovation risk and create new, innovative, and successful products and services.
Product Development at Lipoid
Since the foundation of Lipoid, the new and further development of our company has proceeded in close cooperation with universities, technical colleges, and other scientific institutes in Germany, Europe, and elsewhere. Here, the scientific department of Lipoid at its Ludwigshafen/Rhine headquarters ensures a constant and interdisciplinary exchange of ideas between practice and research. Not only Lipoid’s R&D department and also the independent Phospholipid Research Center, which is generously supported by Lipoid GmbH and PHOSPHOLIPID GmbH, promote the exchange of ideas between science and industry.