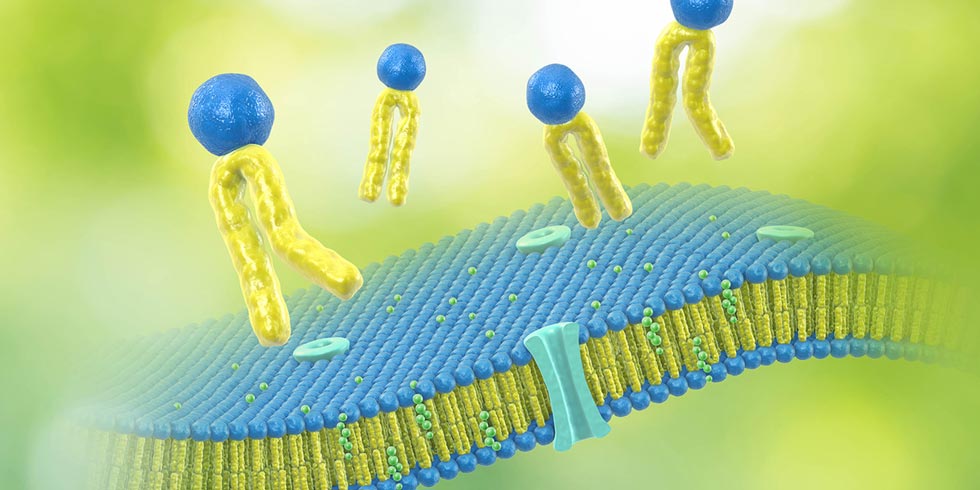
What is Phosphatidylcholine?
Phosphatidylcholine is the fat-soluble form of the vitamin-like substance choline and an important phospholipid for the human body. The molecule consists of a water-soluble choline head and two fat-soluble fatty acids including polyunsaturated ones. Phosphatidylcholine exhibits antioxidative properties, can reduce inflammation and enhance cell membrane integrity.
Furthermore, positive hepatoprotective effects of these fatty acids could be demonstrated in several clinical studies.
Current Supply Situation in the Population
High phosphatidylcholine content can be found in animal-derived food such as meat, eggs, fish and milk or in breast milk. Plant-derived foods contain comparatively low amounts of phosphatidylcholine. The recommended daily intake of choline set by the FDA is 550 mg/day for men and 425 mg/day for women. Pregnant and lactating women have a further increased need for choline of 450 g/day and 550 mg/ day respectively. Nowadays, most population groups do not reach the recommended choline intake.
Choline occurs in various supplementation forms, including synthetic choline bitartrate and natural phosphatidylcholine. The natural form is widely present in animal and plant cells, as well as in breast milk. To provide this valuable form of choline, Lipoid offers high-quality phosphatidylcholine from natural sources like soybeans or sunflowers.
The benefits of natural phosphatidylcholine over artificial choline salts:
- Phosphatidylcholine can be efficiently processed by the body via natural pathways to form new cell structures
- Phosphatidylcholine has an enhanced bioavailability and faster absorption
- Due to the effective natural uptake, phosphatidylcholine does not reach the large intestine and therefore is not converted into transmethylamine-N-oxide (TMAO) by gut microbes
- In addition to choline, phosphatidylcholine provides essential unsaturated fatty acids that contribute to its health benefits